The Faculty of Agriculture at Universitas Gadjah Mada (Faperta UGM), in collaboration with Kasetsart University, Thailand, held an open guest lecture for the UGM academic community and the general public on Wednesday, June 4, 2025. The lecture was delivered online via Zoom Meeting by Dr. Chanita Boonmak from the Duckweed Holobiont Resource and Research Center (DHBC), Kasetsart University, Thailand.
The lecture, titled “Duckweed Microbiome: Unlocking Bacterial Potential for Environmental and Food Applications”, presented research findings from a collaborative project funded by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) and the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) under the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) program.
Thailand is home to four duckweed genera: Spirodela polyrhiza, Landolita punctata, Lemna aequinoctialis, and Wolffia globosa. Dr. Chanita explained, “Duckweed’s nutritional content varies depending on its environment. It contains fiber, lignin, protein ranging from 7–45%, and starch between 14–44%, all of which can be utilized by humans.” In Thailand, duckweed is cultivated for various purposes: Wolffia grown in clean water is used as livestock feed to improve egg yolk quality, it acts as a carbon sequestration agent by rapidly absorbing CO₂, serves as a starch substrate for biofuel, and can be processed into bioplastics and polyester.
“Duckweed’s high protein content is influenced by environmental conditions. It’s a fast-growing aquatic plant that requires minimal space but offers significant benefits for water and land ecosystems,” she added. According to her research, duckweed can thrive on water surfaces such as rice fields, lotus ponds, drying canals, and natural ponds. It can also grow in polluted or wastewater environments, including urban areas and designated wastewater ponds.
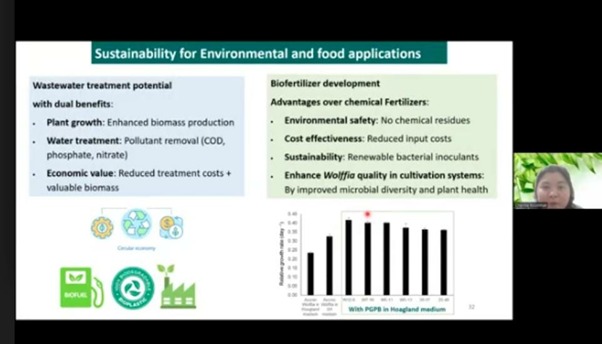
To enhance duckweed growth in wastewater streams, Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria (PGPB) can be utilized. Common bacterial phyla found in association with duckweed include Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, Betaproteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Actinobacteria. Agricultural waste, particularly from livestock farming, often contains high organic matter such as chicken manure, feed, feathers, and wash water, typically treated in anaerobic wastewater tanks. However, nitrogen removal can be challenging, requiring additional treatment such as facultative ponds planted with duckweed.
Desi Utami, S.P., M.Env.Sc., Ph.D., a lecturer in Agricultural Microbiology and coordinator of the guest lecture, emphasized that this regular international lecture series aims to broaden students’ knowledge, spark curiosity, and foster global collaboration for Faperta UGM.
Through partnerships with Kasetsart University and Hokkaido University, Faperta UGM is expanding its understanding of duckweed and its vast potential for sustainable applications. This initiative also supports the achievement of several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDG 1: No Poverty, SDG 2: Zero Hunger, SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being, SDG 14: Life Below Water, SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions, and SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals.
Writer: Octavia Riezqi Yusandra
Editor: Desi Utami
Documentation: Media Faperta